
Back
Important Points When Installing Guest OS
This page describes points to note when installing a guest OS on a virtual machine.
Linux Installation Precautions
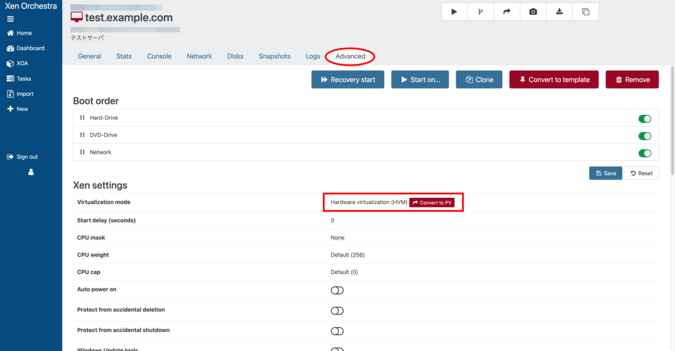
Set the Virtualization mode to Hardware virtualization (HVM) [Only for older Linux OS]
When installing an older Linux OS, it is recommended to change the Virtualization mode from PV to HVM before installation .
Before starting the installer, open the “Advanced” tab of the virtual machine on which you will install the guest OS. Make sure that the “Virtualization mode” field in “Xen settings” is set to “Hardware virtualization (HVM)”. If it is set to “Paravirtualization (PV)”, click “Convert to HVM” and change it to “HVM”. This change must be made before installing the OS. If you make this change after installing the OS, you will not be able to start the OS.
After the OS installation is complete, the system will switch to PV-HVM mode after installing the PV Driver.
Why you shouldn’t use PV mode
“Paravirtualization (PV)” mode has been around since the early days of Xen, and is a mode that allows a unique Linux kernel to run with memory management and IO management replaced with Xen hypervisor calls. On the other hand, HVM mode is a mode that emulates hardware, and PV ran faster than HVM when it was implemented. For this reason, the default installation set for older Linux OSs may be PV.
Later, with the addition of various virtualization instructions to the CPU (Intel-VT and AMD-V instruction sets), PV-HVM mode was created. PV-HVM mode is based on HVM mode, but leaves IO and memory management to the CPU’s virtualization instructions, and compared to PV mode, it has improved execution speed and higher isolation for each virtual machine. It also improves the portability of virtual machine images (ease of moving to other hypervisors). PV-HVM mode is a mode that starts in HVM mode and automatically changes when the PV Driver is installed in the virtual OS.
Currently, there is little value in using PV mode, and it has been pointed out that it is susceptible to security holes inherent in CPUs, such as Spectre and Meltdown.
EXT file systems are not recommended
Generally, it is not recommended to use “ext2/3/4” as a file system.
Generally, virtualized systems often share storage, and when a virtual machine generates a large amount of I/O, it affects other virtual machines housed in the same location. This causes storage delays and this problem occurs. If you select the IaR type for the High Response Private Cloud Xen type, local storage is used, making this problem less likely to occur, but it can occasionally occur during live migration, etc.
Notes on installing Windows
Turn off defragmentation
In the Xen environment at HRPC, the Windows defragmentation process is currently ineffective in all combinations. Please disable defragmentation.
 Japan
Japan Korea
Korea China
China Taiwan
Taiwan Vietnam
Vietnam Thailand
Thailand Indonesia
Indonesia Portugal
Portugal Spain
Spain France
France Germany
Germany Egypt
Egypt Russia
Russia
